BLOG – GYNECOLOGIC CANCERS
- Home
- Blog
- Gynecologic Cancers
- Feb,1 2022
Gynecologic Cancers
Humans represent the most complex form of life. A lot of processes happen in the human body. Some basic processes are metabolism, responsiveness, organization and more. Additionally there is growth, digestion etc which are all very interrelated. All function together, in balance, for the well being of the individual. A disruption in the balance can create havoc in the body.
Cell division is one such controlled process where cells grow & multiply to form new cells. When cells grow old or become damaged, they die, and new cells take their place. When these cells instead grow uncontrollably and start spreading to other parts of the body, it is called cancer.
There are over a 100 types of cancer mostly named based on the body part where the cancer starts. Among these gynecological cancers are quite common. Gynecological cancer refers to cancers that start in a woman’s reproductive system. Cervical cancer, Ovarian cancer, Vaginal cancer, Vulvar cancer and Endometrial cancer are all gynecological cancers.
Cervical cancer
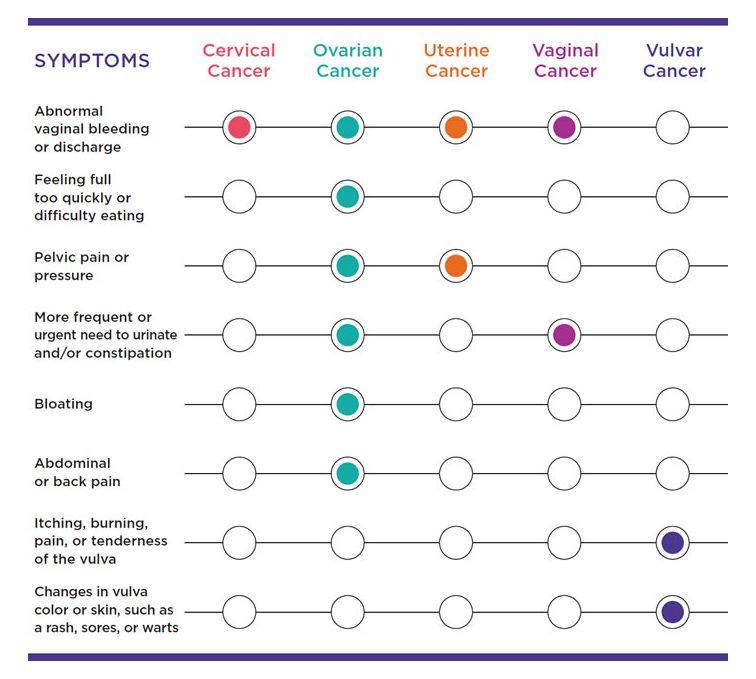
Cervix is a cylinder-shaped neck of tissue that connects the vagina and uterus. It is located at the lowermost portion of the uterus. When cancer affects the cells of the lining of the cervix it is called cervical cancer. It is caused by the Human Papilloma Virus. It is a sexually transmitted virus which may not necessarily affect everybody. In some cases the virus can remain in the body for years and cause some cells to turn into cancer cells. Cervical cancer doesn’t immediately show symptoms. Vaginal bleeding post intercourse, foul smelling watery vaginal discharge and pelvic pain and some symptoms that show in advanced stages. Some risk factors for cervical cancer includes smoking, having intercourse early in life, having multiple partners, other sexually transmitted infections, a weakened immune system etc. Regular screening, HPV vaccine, quitting smoking and practicing safe sex are some ways to prevent cervical cancer. Depending on the stage of the cancer, surgery, radiation, chemotherapy or a combination of treatments may be used to treat cervical cancer.
Ovarian cancer
Women have two ovaries, one on each side of the uterus. Ovaries are responsible for releasing eggs for reproduction. Ovaries also produce hormones estrogen and progesterone. Ovarian cancer is a growth of cells that form the ovaries. There are some symptoms which ovarian cancer shows but it could be similar to several other conditions. Abdominal bloating or swelling, quickly feeling full when eating, weight loss discomfort in the pelvic area, fatigue, back pain, changes in bowel habits, such as constipation, frequent need to urinate etc are some of the symptoms. Some risk factors for ovarian cancer includes age, family history, genes, being obese, endometriosis, never having been pregnant etc.
Prevention of ovarian cancer may be possible through genetic testing and preventive surgery. But one cannot have children after having ovaries removed. So it might be ideal for people who have crossed child-bearing years or for people who had children already.
Vaginal cancer
Vaginal cancer is cancer cells that occur in the vagina. This is rare. Cancer usually spreads to the vagina from elsewhere but cancer that began from the vagina might be difficult to treat. Unusual vaginal bleeding, watery vaginal discharge, a lump or mass in the vagina, painful & frequent urination, constipation, pelvic pain etc are all the usual symptoms of vaginal cancer. Usual risk factors include age, smoking, multiple partners, early sex etc. Vaginal cancers can be dangerous since they can spread to other parts of the body. One type of vaginal cancer is caused by Human Papilloma Virus for which vaccination is a solution. Regular screening, not smoking etc are all important to prevent vaginal cancer. Radiation therapy, chemotherapy, surgery are all the treatment options for vaginal cancer.
Vulvar cancer
Vulvar cancer is cancer that occurs on the outer surface area of the female genitalia.
Vulvar cancer commonly forms as a lump or sore on the vulva that often causes itching. Though it can occur at any age, vulvar cancer is most commonly diagnosed in older adults. Some symptoms that vulvar cancer shows are itching that doesn’t go away, pain and tenderness, bleeding that isn’t from menstruation, skin changes, such as color changes or thickening, a lump or an open sore. Similar to other gynaecological concerns vulvar cancer may be caused due to smoking, unprotected sex and subsequent HPV infection, smoking and age factors. It mostly requires surgical removal of cancerous cells but sometimes might require the entire vulva to be removed. Other treatments like radiation, chemotherapy etc may be combined.
Endometrial cancer
Endometrial cancer is cancer that develops in the uterus. Uterus is where a fertilized egg grows into a baby. This type is also called uterine cancer. The most common symptom of this cancer is unusual vaginal bleeding which makes it detectable at an early stage. Mostly when detected early and removed this type of cancer gets cured. Other symptoms of this disease include pelvic pain and bleeding after menopause. Risk factors of endometrial cancer include fluctuations in balance of hormones, not having been pregnant, older age, obesity etc. More years of menstruation is also a risk factor. Which means if someone attained puberty early & hits menopause late, exposing the endometirum to estrogen for a longer period of time, they may be prone to this type of cancer. Maintaining a healthy weight helps in preventing endometrial cancer. Women who undergo hormone replacement to deal with menopause symptoms should talk to their doctor about the risk of being affected by this type of cancer. Like other cancers, this may also involve surgery, radiation therapy etc.
Cancer is a deadly disease. Early detection in any type of cancer could help in better treatment and increase the lifespan of the person affected. Cancer spreads from one organ to another and with proper treatment, that can be controlled. With proper methods towards prevention like weight management, HPV vaccination, regular screening etc cancer can be eliminated to a large extent.

