BLOG – WHAT IS BRONCHITIS?
- Home
- Blog
- What Is Bronchitis?
- Nov,1 2021
What Is Bronchitis?
Bronchitis is when the tubes that carry air to your lungs, called the bronchial tubes, get inflamed and swollen. You end up with a cough and mucus.
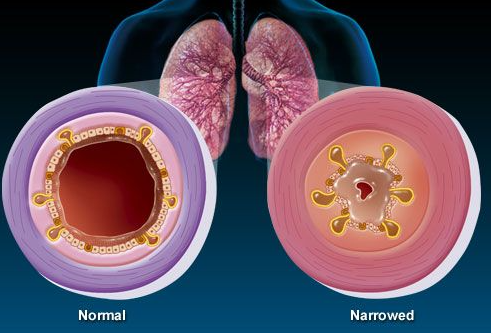
What are the types of Bronchitis?
There are two types:
Acute bronchitis. This is more common. Symptoms last a few weeks, but it doesn’t usually cause problems past that time.
Chronic bronchitis. This one is more serious. It keeps coming back or doesn’t go away.
What are the symptoms of Bronchitis?
Symptoms of both acute and chronic bronchitis include breathing problems, such as:
- Chest congestion, when your chest feels full or clogged
- A cough that may bring up mucus that’s clear, white, yellow, or green
- Shortness of breath
- Wheezing or a whistling sound when you breathe
Symptoms of acute bronchitis also may include:
- Body aches and chills
- Tiredness
- Low fever
- Runny, stuffy nose
- Sore throat
Even after the other symptoms of acute bronchitis are gone, the cough can last a few weeks while your bronchial tubes heal and the swelling goes down. If it goes on much longer than that, the problem might be something else.
What are the causes of Bronchitis?
Most often, the same viruses that give you a cold or the flu cause acute bronchitis. But sometimes, bacteria bring it on.
In both cases, as your body fights the germs, your bronchial tubes swell and make more mucus. That means you have smaller openings for air to flow through, which can make it harder to breathe.
Chronic bronchitis causes include:
- Breathing in air pollution and other things that bother your lungs, like chemical fumes or dust, over time
- Smoking or breathing in secondhand smoke for a long time
What are the risk factors of Bronchitis?
You have a higher chance of getting either kind of bronchitis if:
- You smoke.
- You have asthma and allergies.
- You have a weaker immune system. This is sometimes the case for older adults and people with ongoing diseases, as well as for babies and young children. Even a cold can make it more likely, since your body’s already busy fighting those germs.
Your risk of getting chronic bronchitis is higher if:
- You’re a female smoker. You may be more at risk than a male smoker.
- You have a family history of lung disease.
What are the tests that will be usually ordered by doctors for Bronchitis?
Here are some of the tests
- Chest X-ray. If you have a fever or had one recently, this can help rule out or confirm pneumonia.
- Sputum culture. If your symptoms are severe, your doctor might get a sample of the mucus you cough up (sputum). A lab test can tell whether the mucus is caused by an allergy or whooping cough (pertussis), which is a very contagious bacterial infection. Serious symptoms may also mean another test.
- Spirometry. This is a test of your lung function. It measures how much air your lungs can hold and how quickly you can blow it all out. The test can help your doctor find out whether you have asthma or another breathing problem, along with your bronchitis.
Tips to prevent Bronchitis?
- Wash your hands regularly.
- Stay away from cigarette smoke & smoking.
- Take timely shots of flu vaccine
- Wearing a face mask could prevent direct exposure to bacteria & viruses to some extent.
- Take adequate fluids & rest

